IBM's nice white paper, which I briefly touched on before, describes a model for mapping how customers make decisions in a given setting. It looks at three types of retail-outlets: Grocery, consumer-electronics, and apparel (clothing), and explains how each type of store has different types of customers, with different motives for visiting, and different in-store behaviour.
For instance, with grocery-shoppers, they map two types of shoppers, those that shop for replenishment and those that shop for convenience. The figure below shows the different reasons why they would visit a store and what they value inside the store: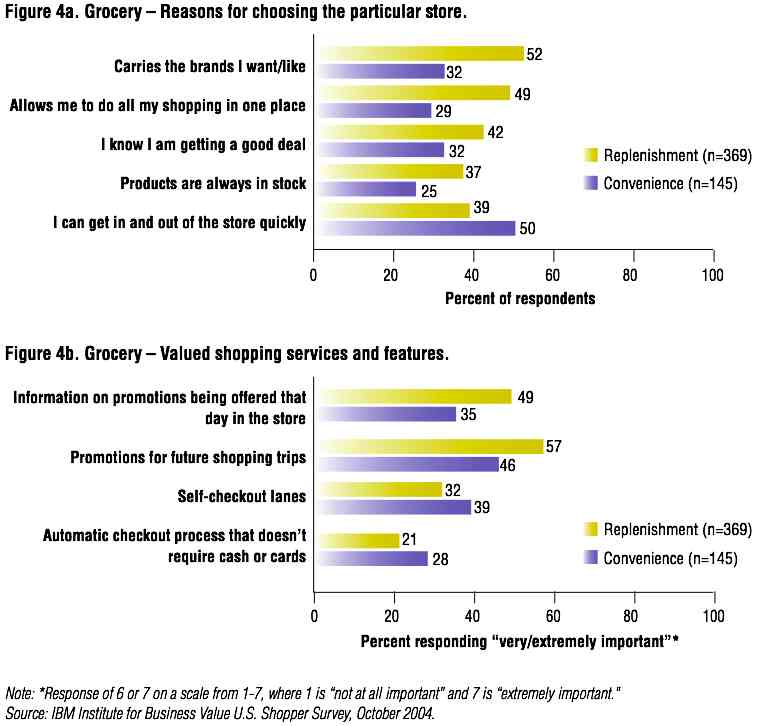
Really, what this flows out of is an analytical technique, IBM calls: "consumer decision process (CDP) modelling," which analyses consumers in five phases:
- Qualitative market research, to identify elements that impact target decisions: what, who, when, where.
- Create individual CDP maps and organise elements into stages
- Validate and create a market-representative view
- Develop quantitative model to prioritise impact of 100s of "why" elements
- Leverage CDP insights to drive revenue opportunities
For instance, in the case of customers for complex electronics, like high-end sound-systems, customers would benefit from a focus on education at the beginning of the decision-making process, and on a high level of technical support after the purchase had been made. This has implications on staffing and marketing. At the same time, this can also affect stock-inventory. With products like these, where people prefer home-deliver and possibly installation, it is often not necessary to carry large amounts of stock within the store, again reducing costs on that front.
Note: this article will be mirror-posted on Tech IT Easy.
Filed under: business strategy, customers, human resources, management, marketing, operation, Research, retail, supermarkets, technology, tools
For instance, with grocery-shoppers, they map two types of shoppers, those that shop for replenishment and those that shop for convenience. The figure below shows the different reasons why they would visit a store and what they value inside the store:

Really, what this flows out of is an analytical technique, IBM calls: "consumer decision process (CDP) modelling," which analyses consumers in five phases:
- Qualitative market research, to identify elements that impact target decisions: what, who, when, where.
- Create individual CDP maps and organise elements into stages
- Validate and create a market-representative view
- Develop quantitative model to prioritise impact of 100s of "why" elements
- Leverage CDP insights to drive revenue opportunities
For instance, in the case of customers for complex electronics, like high-end sound-systems, customers would benefit from a focus on education at the beginning of the decision-making process, and on a high level of technical support after the purchase had been made. This has implications on staffing and marketing. At the same time, this can also affect stock-inventory. With products like these, where people prefer home-deliver and possibly installation, it is often not necessary to carry large amounts of stock within the store, again reducing costs on that front.
Note: this article will be mirror-posted on Tech IT Easy.
 The
The 

